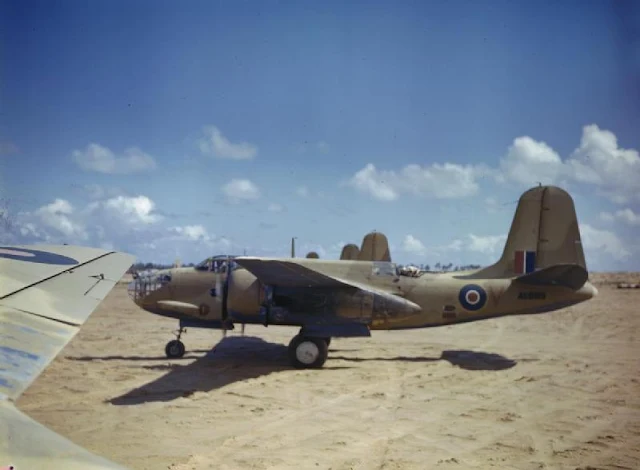
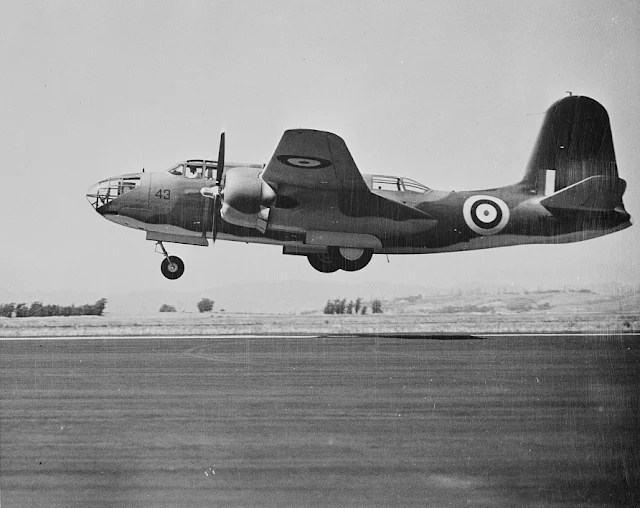
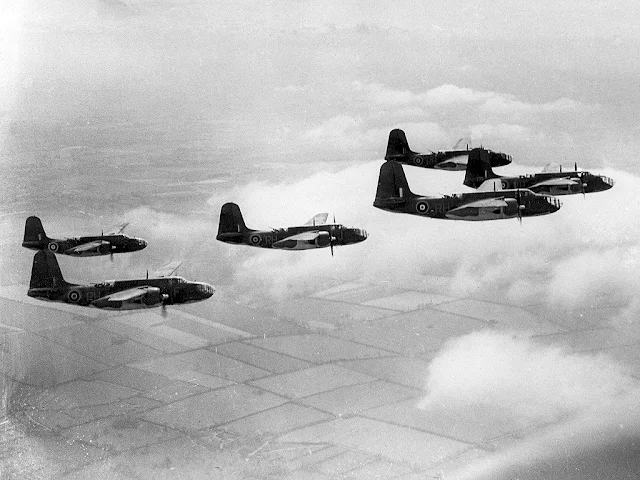
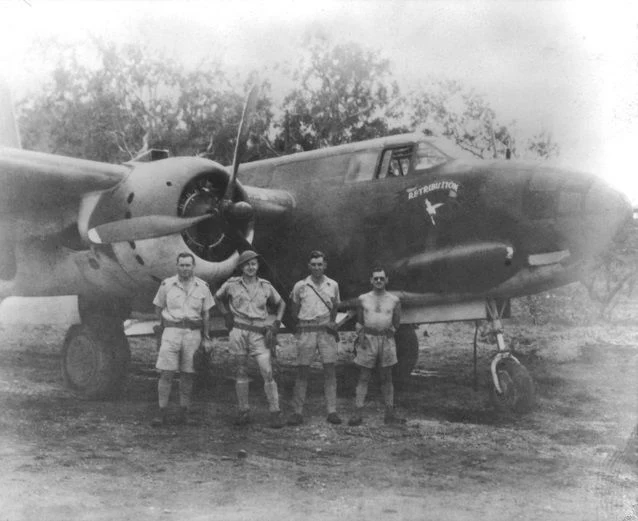
|
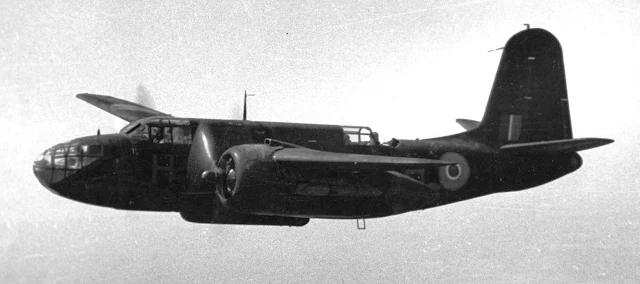
| Bréguet 462. |
The Bréguet 460 Vultur was a French bomber of the 1930s. Few
of these twin-engined monoplanes and its variant, the Bréguet 462 Vultur, were
built. At least one Bréguet 460 was sold to the Spanish Republican Air Force
during the Spanish Civil War.
The Bréguet 460 was a light bomber initially based on the
plane type labeled as Multiplace de Combat, a multi-functional aircraft, by the
French aviation authorities. Eventually the prototype was modified in 1934
departing from the parameters set for its predecessor, the Bréguet 413, in
order to meet the requirements of a high-speed bomber for the French Air Force.
The resulting plane was a monoplane fitted with two powerful
radial Gnome et Rhône 14Kjrs engines and had more aerodynamic appearance,
although it kept the tail of the obsolete Bréguet 413. Owing to technical
difficulties production was delayed and when the first prototype of the Bréguet
460 Vultur flew it could not achieve the 400 km/h (250 mph) required for a high
speed bomber. Thus the French Air Ministry lost interest in this unit and
concentrated on projects by other companies such as the Amiot 340 and the LeO
45. These planes, however, would not be ready until three years later.
The outbreak of the Spanish Civil War provided the French
aircraft industry with a good opportunity both for getting rid of obsolete
aircraft and for testing new developments. Therefore it is in this context that
the Bréguet 460 prototypes ended up in the Spanish Republican Air Force. One of
the units seen in a picture of the Spanish conflict has an improved, more
modern tail of the same type that would be used later for the Bréguet 470
Fulgur airliner.
The number and the fate of the Bréguet 460 Vultur units in
the Spanish Republican Air Force are obscure as is common with most of the
flying units of the loyalist air arm during the conflict. It is known that one
of these aircraft was based at the Celrà airfield towards the end of the
conflict and that it belonged to the Night Flight Group no. 11, which comprised
the Vultur and two Bloch MB.210. This particular Bréguet 460 crashed in the sea
near L’Escala and all the crew perished in the crash.
The Bréguet Bre.462 was a modernized version of the Bréguet
460, although still very similar, that made its first test flight towards the
end of 1936. The front part of the fuselage was redesigned to look more
aerodynamic and the plane was fitted with two Gnome Rhone 14NO engines that
allowed it to reach a speed of 402 km/h (250 mph). Flight described it as
similar to the Bréguet 461 that was supplied to Japan in 1935 A planned
installation of 1,350 hp engines was expected to give it a speed of around 300
mph. Bombload was 1076 kg. Defensive armament was a forward-firing 20 mm cannon
and two rear-firing machine guns.
Only three Bréguet 462 were built. Two of them served in the
Vichy French Air Force where they didn’t see much action. They ended up being
scrapped in 1942.
Role: Bomber
aircraft
National
origin: France
Manufacturer:
Breguet Aviation
First flight:
1935
Crew: 5
Length: 12.84 m
(42 ft 2 in)
Wingspan: 20.58
m (67 ft 6 in)
Height: 4.10 m
(13 ft 5 in)
Wing area: 60
m2 (650 sq ft)
Gross weight:
8,200 kg (18,078 lb)
Powerplant: 2 ×
Gnome-Rhône 14Kdrs 14-cylinder air-cooled radial engine, 600 kW (804 hp) 815 cv
each
Maximum speed:
400 km/h (249 mph; 216 kn)
Range: 2,000 km
(1,243 mi; 1,080 nmi)
Service
ceiling: 10,000 m (32,808 ft)
Guns: 1 ×
fixed, forward-firing 20 mm Hispano-Suiza HS.404 cannon, 2 × rearward-firing
machine guns
Bombs: 1076kg
Variants
Bre.460: Light bomber and strike
aircraft with two Gnome-Rhône 14Kdrs1 radial engines. One prototype built.
Bre.460 M5: 1935 design. Light bomber
and strike aircraft powered by two Gnome-Rhône 14Kdrs radial engines. One
prototype built.
Bre.462 B4: A modernized version of the
Bre.460. Only 3 built
Operators
France: Armée de
l’Air
Spain: Spanish
Republican Air Force
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460 'Vultur'. |
 |
| Bréguet 460 'Vultur'. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460 'Vultur'. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460 'Vultur' of the Spanish Republican Air Force, 1937. |
 |
| Bréguet 460 'Vultur' of the Spanish Republican Air Force, 1937. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-01 on its first flight. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-01. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-01 at Paris Air Show, 13 November 1936. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-02, 1937. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-02, 1937. |
 |
| Cockpit and lower tier of Bréguet 462-02. |
 |
| Cockpit of Bréguet 462-02. |
 |
| View towards the rear of the fuselage of the Bréguet 462-02. |
 |
| Access hatch to the dorsal gun position in the Bréguet 462-02. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-02 with civil registration F-AKIB. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-02 with civil registration F-AKIB. |
 |
| Bre.462 B4 'Vultur' pictured while being jacked up for landing gear cycling tests with running engines. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-02, 1937. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-02, 1937. |
 |
| Bréguet 462-02, 1937. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |
 |
| Bréguet 460-01. |
 |
| Bréguet 460. |