 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
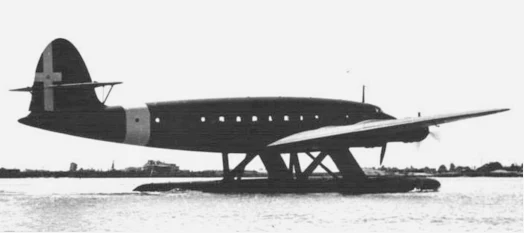
The CANT Z.511 was a four-engine long-range seaplane designed by Filippo Zappata of the "Cantieri Riuniti dell'Adriatico" (CRDA) company. Originally designed for the Central and South Atlantic passenger routes, it was later adapted as a military transport and special raider.
The design for the construction of a large four-engine, twin-float seaplane began at the end of September 1937, when the technical department of CRDA accepted the specifications of the LATI (Compagnia Ala Littoria) company, created in 1939, who required a long-range seaplane for carrying mail, cargo and passengers to Latin America.
These plans were cancelled on the outbreak of World War II, but a version of the aircraft was adapted for long-range maritime patrol, armed with 10 single-mount 12.7 mm (0.500 in) machine guns in both side gun positions, in two upper turrets, and belly positions. Plans were made to install 20 mm (0.787 in) cannon in a front turret or in a glazed nose position, and more machine guns in a tail position.
For bombing, it was adapted to carry up to 4,000 kg (8,800 lb) of bombs in an internal bomb bay and on outer wing positions: up to four launch racks, for 454 mm (17.9 in) air-launched torpedoes for surface attack [citation needed], or "Maiale" manned torpedoes or midget submarines for special operations.
The original engines were relatively underpowered, so Zappata asked the authorities for permission to acquire 1,193 kW (1,600 hp) Wright R-2600 Double Cyclones from the United States. Due to the deteriorating international situation, however, he was unable to obtain authorization. The CANT Z.511 civil aircraft could theoretically carry 16 passengers over 5,000 km (2,700 nmi; 3,100 mi). Later, when adapted as a military transport, four 1,119 kW (1,501 hp) Piaggio P.XII R.C.35 were used, giving only adequate power to an aircraft weighing up to 34 t (75,000 lb), giving it a maximum range of 4,500 km (2,400 nmi; 2,800 mi).
The Z.511 had its first test flights at Monfalcone, Venezia Giulia (north-eastern Italy) between October 1940 and March 1942. Between 28 February and 1 March 1942, test pilot Mario Stoppani succeeded in taking off and landing fully loaded in very rough seas, with 1.5 m (4.9 ft) waves and winds of 55–65 kilometers per hour (30–35 kn; 34–40 mph). The Z.511 prototype was then transported to Grado, Venezia (further away from the insecure Yugoslavian border) for further evaluations; the last test and operational flight occurred on 1 September 1943, two days before the Italian Armistice was signed.
After the division of the Italian forces, one aircraft was appropriated by the Fascist Aeronautica Nazionale Repubblicana. However, it had been damaged only three weeks before by British fighters, which had strafed it on Lake Trasimeno where it was undergoing final trials. It was transferred to the seaplane base at Vigna di Valle. There it suffered from sabotage by base personnel to prevent it falling into the hands of either the Allies or the Germans. The other aircraft, still under construction at the CRDA factory, was retained by Axis forces and scrapped.
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
CANT Z.511. |
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
|
CANT Z.511. |
 |
| CANT Z.511. |
