 |
| A U.S. Marine Corps North American SNJ-3 Texan and a Curtiss SBC-4 Helldiver assigned to the First Marine Air Wing in flight in early 1942. |
 |
| Grumman TBF Avenger torpedo bombers practice a torpedo run during training exercises on the East Coast of the United States. |
 |
| Miles Master Mark III, W8667, '3', of No. 5 Service Flying Training School based at Ternhill, Shropshire, in flight. |
 |
| Supermarine Spitfire prototype (K5054) on its first flight on 5 March 1936. |
 |
| Supermarine Spitfire prototype (K5054). |
 |
| Spitfire prototype (K5054) in camouflage scheme. |
 |
| Spitfire Mk I (K9795) of No. 19 Squadron RAF in 1938. |
 |
| Spitfires of No. 222 Squadron take off during the Battle of Britain. |
 |
| Spitfire Mk VB (BM590 AV-R) of No. 121 Squadron RAF. |
 |
| Seafire Mk IIC (MB156 6G-O) Royal Navy on HMS Formidable. |
 |
| Spitfires of No. 453 Squadron RAAF with invasion stripes. |
 |
| Supermarine Spitfire Mk. I, with RAF aces, No. 92 Sqn., Manston, 1941. |
 |
| Supermarine Spitfire Mk V Trop of 253 and 32 Sqdns. in Cannes. |
 |
| Supermarine Spitfire Mk V Trop of 417 Sqdn. awaiting take-off at Gubin, Tunisia in 1943. |
 |
| A Gloster Meteor in Belgium in early 1945, sent over to counter the Me 262. The Meteors were painted white so they were easy to identify. |
 |
| Bombs explode on the northern dispersal area at Abbeville/Drucat airfield, France, during an attack by 18 Lockheed Venturas of No. 21 Squadron RAF and No. 464 Squadron RAAF. |
 |
| Hawker Hurricanes, Vultee Vengeances and North American Harvards lined up for flight testing after assembly at No. 1 (India) Maintenance Unit, Drigh Road, India. |
 |
| French Lioré et Olivier LeO 451 bomber. |
 |
| Caudron C.714-01. |
 |
| Caudron C.R. 760. |
 |
| Caudron C.R. 770. |
 |
| Caudron C.R. 770. |
 |
| Caudron C.R.760 C.1 |
 |
| Caudron C.R.770. |
 |
| Caudron C.714. |
 |
| Caudron C.710. |
 |
| Caudron C.710. |
 |
| Caudron C.714 cockpit. |
 |
| Caudron C.714 cockpit. |
 |
| Caudron C.714 cockpit. |
 |
| Caudron C.714. |
 |
| Caudron C.714. |
 |
| Caudron C.R.760. |
 |
| Caudron C.R.770. |
 |
| Caudron C.714. |
 |
| Caudron C.713. |
 |
| Caudron C.713. |
 |
| Caudron C.714 after capture by the Germans. |
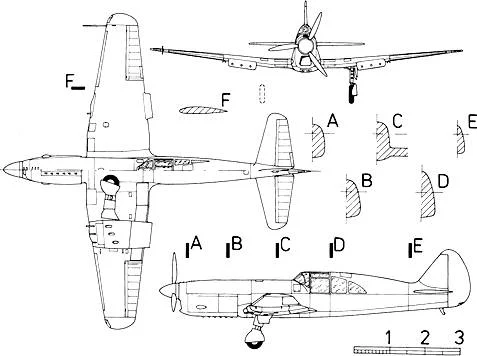 |
| Caudron C.R.760. |
 |
| Caudron C.R.714. |
 |
| Caudron C.R.760. |
 |
| Caudron C.714 in Luftwaffe service. |
 |
| Caudron C.714, Groupe de Chasse I/145. |
 |
| Caudron C.714 fighter plane of Groupe de Chasse I/145, June 1940. |
 |
| Caudron C.714s of Groupe de Chasse I/145 after capture by the Germans. Note that the Polish insignia on the fuselage sides has been cut away. |
 |
| Caudron C.714, Groupe de Chasse I/145. |
 |
| Caudron C.714, Finnish air force. |
 |
| Caudron C.714, Finnish air force. |
 |
| Focke Wulf Fw 191A. |
 |
| Focke-Wulf 191 V-1. |
 |
| Gotha Go 147. |
 |
| Heinkel He 46 BB+CK reconnaissance aircraft. |
 |
| Gotha Go 145A, KE+WF, tandem two-seat training biplane. |
 |
| The fuselage of a German Heinkel He 111 bomber shot down near Hazebrouck being transported on a trailer towed by a French half-track through the town of Roye, November 1939. |
 |
| Heinkel He 111 with V-1. |
 |
| He 111 ready to tow a Go 242 glider, Russia, January 1943. |
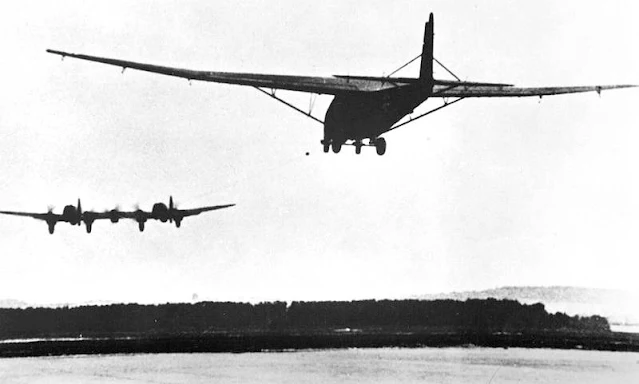 |
| Me 321 being towed by a Heinkel He 111Z. |
 |
| A five-engine Heinkel He 111Z Zwilling (Twin) and, just coming in to land in the background, a six-engine Messerschmitt Me 323 Gigant (Giant), possibly Sicily, 1943 |
 |
| Horten XIII Tailless Aircraft in flight. The crew is in the crew cab at the rear of the aircraft. |
 |
| Horten III-c with added wing foil. The man sitting on the aircraft is identified as Pilot Blech. |
 |
| Horten H Xb (Piernifero II) on its nose on a cart being pulled by a car. |
 |
| Deutsches Luft Hansa (DLH) Junkers F 13 bi "Dommel" (r/n D-582) on the ground, loading passengers; circa 1926-1933. |
 |
| Me 163 variants. |
 |
| Captured Ilyushin Il-4 (earlier designation DB-3F) (DF-25) medium bomber in Finnish service, 1 April 1944. |
 |
| Captured Ilyushin Il-4, Finnish Air Force. |
 |
| Captured Ilyushin Il-4, Finnish Air Force. |
 |
| Captured Il-4 with LaGG-3 in foreground in Finnish service. |
 |
| Captured Ilyushin Il-4 in Luftwaffe service. |
 |
| Captured Ilyushin Il-4 in Luftwaffe service. |
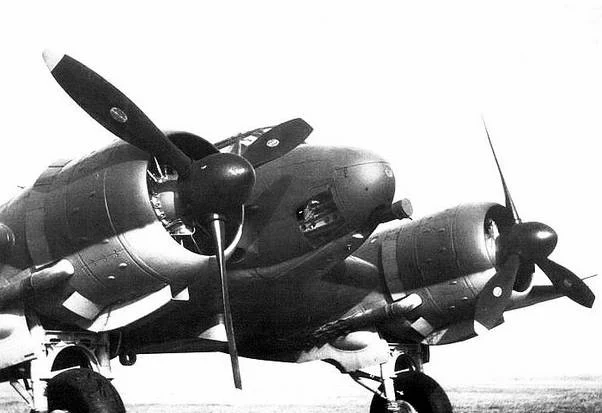 |
| Fiat Cansa FC.20 Regia Aeronautica. |
 |
| 1934 photo of a French Amiot 143. This type was thrown into the battle to destroy the Meuse bridges. |
 |
| Waist gunners on a B-24. |
 |
| French Breguet 690, photographed in July 1939. |
 |
| Ryan STM, S-26, Morokrembangan, Surabaya, circa 1940-41. |
 |
| Ryan STM, S-13, Morokrembangan, Surabaya, circa 1940-42. |
 |
| Schweizer TG-3A (Schweizer SGS 2-12) training glider. |
 |
| Seversky XP-41. |
 |
| Spartan C-71 (42-38367), one of 16 purchased by the Army from private owners. |
 |
| Stinson XR3Q-1, 9718. |
 |
| Stinson XR3Q-1, 9718, NAS Sunnyvale. |
 |
| Maj. Gen. Claire Chennault of Flying Tigers fame, center, at an airfield in Kweilin, China. |
 |
| U.S. Navy Vought O2U-1 Corsair floatplane (BuNo A7819) from Scouting Squadron 6 on the port catapult of the light cruiser USS Concord (CL-10), in 1932. |
 |
| O3U-3 (9300), from the battleship Colorado, visiting Oakland, 1939. |
 |
| Vought XTBU-1 (2542). |
 |
| USAAC 1st Lieutenant standing in front of Vultee BT-13 Valiant basic training aircraft on the ground, at an unidentified flying school somewhere in the United States, circa 1943. |
 |
| Vultee BT-13. |
 |
| Major James A. Elisson returns a salute to Mac Ross, as he reviews the Tuskegee cadets, lined up in front of their training aircraft, a Vultee BT-13, 1941. |
 |
| Vultee BT-13 Valiant. |
 |
| Pilots of F6F-3 Hellcats who shot down 21 Japanese enemy planes in less than 15 minutes over Truk Atoll, 29 April 1944, aboard USS Langley (CVL-27). |








